What is a TPM (Trusted Platform Module) Chip: After the much-awaited Microsoft Window 11 operating system launch event, people wondered when and how the new Windows 11 OS would be available to its users for installation. Microsoft on its website said that it would be available for free to upgrade to its Windows 10 users, but there is a catch as it may not be available to upgrade to all its user. Microsoft also said it is ending support for Windows 10 on October 14th, 2025.
To check this Microsoft has given a PC Health Check tool in its website.
After running this tool, many users must be wondering that even their High-End PC are not eligible for Windows 11 upgrade and were getting below error; the users must be shocked to know the reason. Although Microsoft has fixed the issue, users will now know what component is missing for the upgrade.
Minimum system requirements
| Processor | 1 gigahertz (GHz) or faster with 2 or more cores on a compatible 64-bit processor or System on a Chip (SoC) |
| Memory | 4 GB RAM |
| Storage | 64 GB or larger storage device |
| System firmware | UEFI, Secure Boot capable |
| TPM | Trusted Platform Module (TPM) version 2.0 |
| Graphics card | DirectX 12 compatible graphics / WDDM 2.x |
| Display | 9” with HD Resolution (720p) |
| Internet connection | Microsoft account and internet connectivity required for setup for Windows 11 Home |
One of the primary reason user found is Trusted Platform Module (TPM) version 2.0 as Windows 11 operating system will require the presence of a TPM, which has raised a storm of doubt and uncertainty. What exactly is TPM, and does your PC already have it? Here’s what you need to know.
What is a TPM?
A Trusted Platform Module is an international standard for a secure cryptoprocessor, a dedicated microcontroller designed to secure hardware through integrated cryptographic keys. A microchip is often built into a computer to provide hardware-based security. It can be added later by industrious users who attach the chip to the motherboard. Not all motherboards offer a TPM connector, so you’ll need to research your model first.
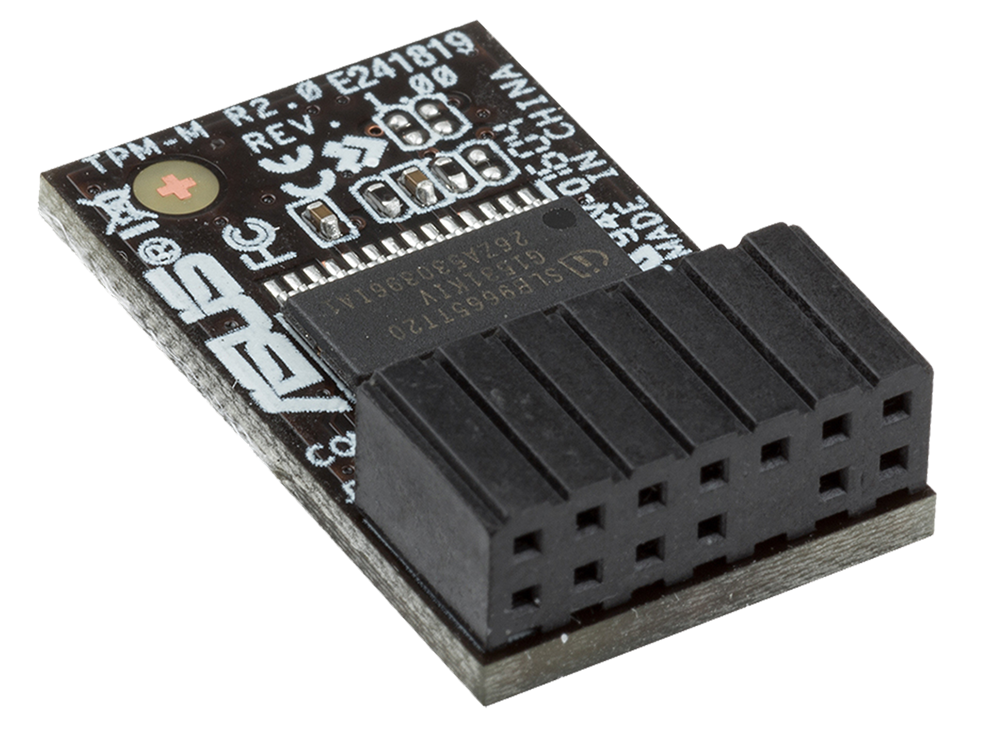
Read How to check the TPM and Enable on your PC
What does a TPM do?
Some, but not all, of the data we transmit throughout the day is sent unencrypted as plain text. TPM chips use software and hardware to protect any critical passwords or encryption keys when they are sent in this unencrypted form.
If a TPM chip senses that a virus or malware has compromised a system’s integrity, it can start up in a quarantine mode to help fix the problem. Some Google Chromebooks include TPMs, and during startup, the chip scans the BIOS (a motherboard firmware that initiates the startup process) for unauthorized changes.
TPM chips also provide safe storage of encryption keys, certificates, and passwords to log in to online services, which is a more secure method than storing them inside software on the hard drive.
TPM chips in network-connected set-top boxes enable digital rights management, so media companies can distribute content without worrying about theft.
Who is TPM for?
While initially targeted at enterprises or larger companies looking to secure their data, TPM chips are now becoming a requirement for all laptops and desktops to ensure security for all users.
There are five different types of TPM 2.0 implementations (listed in order from most to least secure):
Discrete TPMs are dedicated chips that implement TPM functionality in their tamper-resistant semiconductor package. They are theoretically the most secure type of TPM because the routines implemented in hardware should be more resistant to bugs versus routines implemented in software, and their packages are required to implement some tamper resistance.
Integrated TPMs are part of another chip. While they use hardware that resists software bugs, they are not required to implement tamper resistance. Intel has integrated TPMs in some of its chipsets.
Firmware TPMs are firmware-based (e.g. UEFI) solutions that run in a CPU’s trusted execution environment. Intel, AMD, and Qualcomm have implemented firmware TPMs.
Hypervisor TPMs are virtual TPMs provided by and rely on hypervisors, in an isolated execution environment that is hidden from the software running inside virtual machines to secure their code from the software in the virtual machines. They can provide a security level comparable to a firmware TPM.
Software TPMs are software emulators of TPMs that run with no more protection than a regular program gets within an operating system. They depend entirely on the environment that they run in, so they provide no more security than what can be provided by the normal execution environment, and they are vulnerable to their own software bugs and attacks that are penetrating the normal execution environment. They are useful for development purposes.
What can you do with a TPM?
The most basic use for a TPM is to set a login password for your system. The chip will automatically guard that data rather than store it on your hard drive. If a system has a TPM chip, its user can generate and manage cryptographic keys to lock the system or specific files.
Many people use a TPM to enable the Windows BitLocker Drive encryption utility. When you power up a system that features a TPM and BitLocker, the chip runs a series of conditional tests to see if it’s safe to boot up. If a TPM senses the hard disk was moved to another location, as might be the case if it were stolen, it locks the system.
Notebooks with built-in fingerprint readers often keep the recorded fingerprints in the TPM, as its security makes it a responsible location for storage. The chip also enables smart-card readers, which certain companies require for user authentication and login.
Windows 11 and TPMs
Windows 7 and Windows 10 both have extensive support for TPMs. Security features at the operating system level make use of TPMs. TPMs are efficient alternatives to older methods of securing Windows PCs. In fact, since July 2016, Microsoft has required TPM 2.0 support on all new PCs that run any version of Windows 10 for desktop (Home, Pro, Enterprise, or Education). Likewise, Windows 11 will only run on PCs that have TPM capabilities. Microsoft has been strict on this requirement ahead of the Windows 11 general availability, which is scheduled to arrive as a free upgrade for Windows 10 PCs this holiday season. If you download the Windows 11 compatibility tool now, it will only indicate that your system is ready if TPM 2.0 is up and running.
Does My PC Already Have TPM 2.0?
If you’ve got a computer that meets the other Windows 11 minimum system requirements, there’s a chance that it supports TPM 2.0. The standard is relatively recent, however. If you bought your PC after 2016, it almost certainly comes with TPM 2.0. If your computer is older than a few years, it likely has the more senior TPM 1.2 version (which Microsoft says is not recommended for Windows 11) or has no TPM.
Some more FAQ
What does TPM protect against?
TPM chips use software and hardware to protect any critical passwords or encryption keys when they are sent in this unencrypted form. If a TPM chip senses that a virus or malware has compromised a system’s integrity, it can start up in a quarantine mode to help fix the problem.
Can TPM be hacked?
In the case of physical access, computers with TPM are vulnerable to cold boot attacks as long as the system is on or can be booted without a passphrase from shutdown or hibernation, which is the default setup for Windows computers with BitLocker full disk encryption.
What is TPM state in BIOS?
A Trusted Platform Module (TPM) is a specialized chip on an endpoint device that stores RSA encryption keys specific to the host system for hardware authentication. The pair is maintained inside the chip and cannot be accessed by software.
Can I turn off TPM in BIOS?
Boot the computer using F2 or any other key (depending on your Manufacturer) into the BIOS setup mode. Locate the “Security” option on the left and expand. Locate the “TPM” option nested under the “Security” setting. To clear the TPM, you must check the ” Clear ” box to remove the TPM hard drive security encryption.
What happens if I disable TPM?
You can disable the TPM, it will remain owned, and secrets will be kept stored. The device will not be detected or usable, or reset. For instance, if you want to boot another operating system temporarily without it being able to alter or own the TPM.


